Sam Robson
Lead Bioinformatician at the Centre for Enzyme Innovation
Centre for Enzyme Innovation, University of Portsmouth
Biography
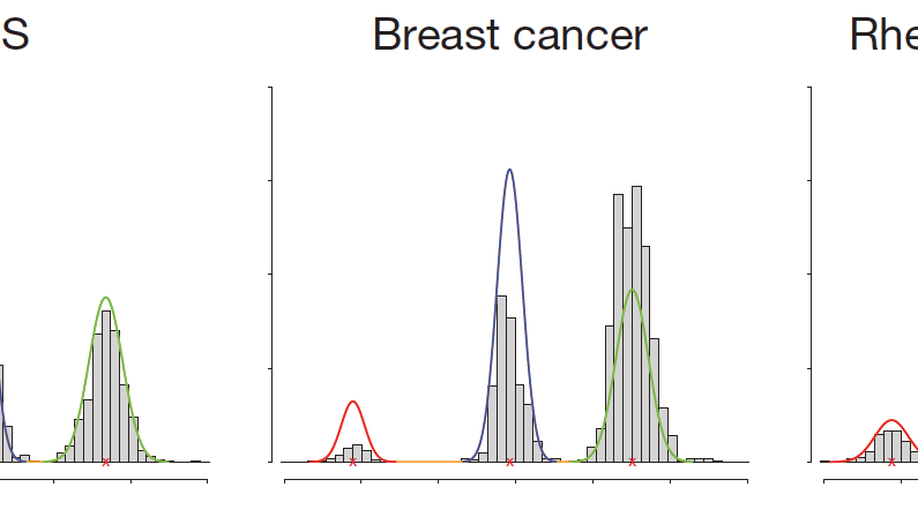
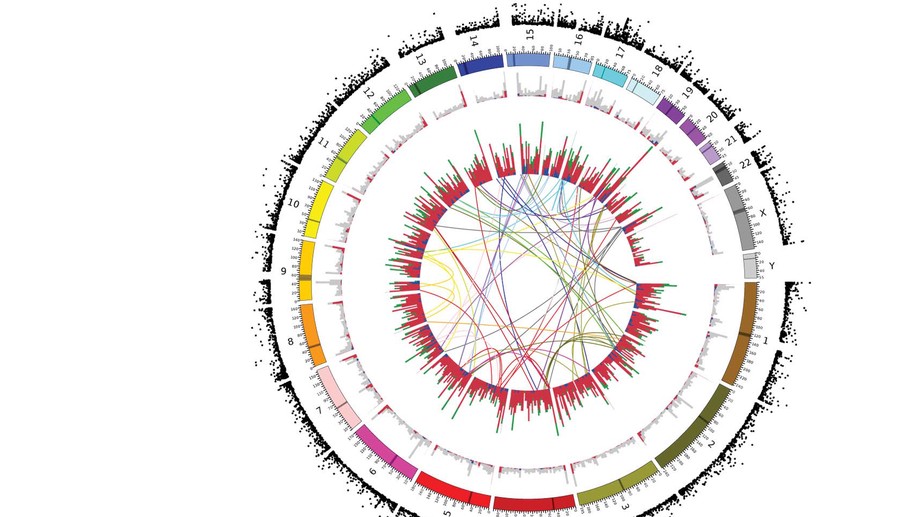
Dr. Sam Robson is a Senior Research Fellow at the University of Portsmouth and is the Bioinformatics Lead at the Centre for Enzyme Innovation. He is a data scientist and computational biologist with an extensive publication history (including 6 Nature papers) and particular expertise in maintenance, processing and analysis of large whole genome sequencing data sets. Previous to his appointment, he worked as a Bioinformatician in the group of Prof. Tony Kouzarides at the Wellcome Trust/CRUK Gurdon Institute. The main research focus of the lab was to analyse the role of histone and RNA modifications, and in particular their role in diseases such as cancer. Prior to this, he held a Post-Doctoral Fellowship at the Wellcome Trust Sanger Institute in the lab of Dr. Matt Hurles. This work focused on the analysis of large scale copy-number variations in the human genome and their role in common diseases such as breast cancer and Crohn’s Disease. His background is in pure Mathematics having achieved his Bachelor’s degree at the University of Warwick, and he holds a Masters and PhD in Mathematical Biology and Biophysical Chemistry from the MOAC Doctoral Training Centre. He is a Professional Member of the International Society for Computational Biology and a Fellow of the Royal Statistical Society and holds CStat and CSci Professional qualifications.
Bioinformatics Group
The Bioinformatics Group at the University of Portsmouth was formed in 2017 by Dr. Sam Robson. We collaborate across the faculty on research projects utilising powerful techniques such as high-throughput sequencing, which require extensive processing and rigorous statistical analyses. We also work to build bioinformatics tools for use by the wider research community. We work on a variety of different projects and data sets, in diverse fields such as environmental biology, marine biology, microbiology, clinical research projects and paleogenomics.
Bioinformatics Computing
The University of Portsmouth hosts a Bioinformatics-specific compute cluster, with well-maintained pipelines for RNA-seq, ChIP-seq, CLIP-seq, BS-seq, Exome-seq, amplicon sequencing, and other sequencing data types used by researchers throughout the University. The cluster consists of 4 compute nodes and 1 head node. The compute nodes consist of Dell PowerEdge R630 Servers with Intel Xeon E5-2650 v4 Processors (12 cores, 2.2GHz), 128GB RAM and 2x 240GB flash (SSD) storage. This provides a total of 48 cores, or 96 threads (via Hyperthreading). The head node is a Dell PowerEdge R630 Server with 2x Intel Xeon E5-2650 v4 Processors (12 cores, 2.2GHz), 384GB RAM and 2x 240GB flash (SSD) storage. Local storage is provided by a Synology RS3617RPxs NAS Server with 120TB HDD storage, connected to the compute nodes via a 10GbE Network. We also use both Amazon Web Services (AWS) and Google Cloud Platform for cloud computing resources.
Interests
- Bioinformatics
- Next generation sequencing
- Mathematics and Statistics
- Machine learning and AI
- Data science
- Programming
- Data curation
Education
-
PhD in Mathematical Biology and Biophysical Chemistry, 2008
University of Warwick
-
MSc in Mathematical Biology and Biophysical Chemistry, 2004
University of Warwick
-
MSc in Mathematics (Hons), 2003
University of Warwick